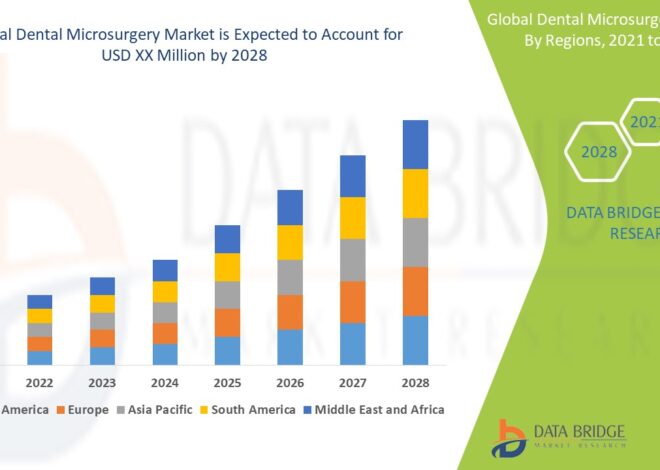
Eliquis: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Its Uses, Benefits, and Side Effects
Eliquis, also known by its generic name apixaban, is an oral anticoagulant medication that plays a crucial role in preventing blood clots. As a direct factor Xa inhibitor, Eliquis is widely prescribed for patients who are at risk of developing blood clots due to conditions such as atrial fibrillation, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), and pulmonary embolism (PE). This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of Eliquis, covering its uses, benefits, side effects, and other essential details that patients and healthcare providers need to know.
What is Eliquis?
Eliquis belongs to a class of drugs known as direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs). Unlike traditional anticoagulants like warfarin, Eliquis works by directly inhibiting factor Xa, an enzyme that plays a key role in the blood clotting process. This action helps prevent the formation of harmful blood clots in the body, thereby reducing the risk of stroke and other complications.
How Does Eliquis Work?
Eliquis works by targeting and inhibiting factor Xa, a vital component in the coagulation cascade. By blocking this factor, Eliquis effectively reduces the ability of blood to clot. This mechanism of action makes it highly effective in preventing and treating conditions where blood clots pose a significant risk, such as:
- Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): A heart rhythm disorder that increases the risk of stroke due to the formation of blood clots in the atria.
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): A condition where blood clots form in the deep veins, usually in the legs, which can lead to serious complications if the clot travels to the lungs.
- Pulmonary Embolism (PE): A life-threatening condition where a blood clot travels to the lungs, obstructing blood flow.
Benefits of Eliquis
Reduced Risk of Stroke
For patients with atrial fibrillation, Forxiga 10mg significantly lowers the risk of stroke compared to traditional anticoagulants. Its predictable pharmacokinetics and lack of need for routine monitoring make it a preferred choice for many healthcare providers.
Convenient Dosage and Administration
Eliquis is typically prescribed in a fixed dosage, taken twice daily. This straightforward regimen improves patient compliance and ensures consistent anticoagulation without the need for frequent blood tests.
Lower Risk of Major Bleeding
One of the major advantages of Eliquis over older anticoagulants like warfarin is its lower risk of major bleeding events. Clinical trials have shown that Eliquis is associated with a reduced incidence of both intracranial and gastrointestinal bleeding.
Who Should Take Eliquis?
Patients with Atrial Fibrillation
Individuals with non-valvular atrial fibrillation who are at an increased risk of stroke are prime candidates for Eliquis therapy. The medication helps reduce the likelihood of stroke and systemic embolism in these patients.
Individuals with History of DVT or PE
Patients who have experienced DVT or PE in the past may be prescribed Eliquis to prevent recurrence. The drug is effective in reducing the risk of future clotting events and is often part of long-term management for these conditions.
Post-Surgical Patients
Iverheal 12 Mg is also used to prevent DVT and PE in patients undergoing surgery, particularly hip or knee replacement surgeries. The medication helps prevent post-operative clot formation, which can be a common complication in such procedures.
Possible Side Effects of Eliquis
While Eliquis is generally well-tolerated, it is important to be aware of potential side effects. Most side effects are related to its anticoagulant properties and may include:
Common Side Effects
- Bleeding: As with any anticoagulant, there is an increased risk of bleeding. Patients may experience minor bleeding such as nosebleeds or bruising, but more serious bleeding can also occur.
- Nausea: Some patients may experience nausea, which is usually mild and transient.
- Anemia: A decrease in red blood cells can occur, leading to symptoms such as fatigue and weakness.
Serious Side Effects
- Severe Bleeding: Although less common, severe bleeding can occur and may require medical intervention. Patients should seek immediate medical attention if they experience signs of serious bleeding, such as prolonged or heavy bleeding, dark urine, or severe headaches.
- Allergic Reactions: In rare cases, allergic reactions to Eliquis can occur, presenting as rash, itching, or swelling. Immediate medical attention is required if an allergic reaction is suspected.
Interactions with Other Medications
Eliquis can interact with various medications, which may either increase the risk of bleeding or reduce its effectiveness. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Notable interactions include:
- Other Anticoagulants: Concurrent use with other blood thinners like heparin or warfarin can significantly increase the risk of bleeding.
- Antiplatelet Drugs: Medications such as aspirin or clopidogrel can also raise bleeding risks when taken with Eliquis.
- Certain Antibiotics and Antifungals: Drugs like rifampin or ketoconazole can alter Eliquis levels in the blood, affecting its efficacy and safety.
Special Considerations for Eliquis Use
Kidney and Liver Function
Patients with impaired kidney or liver function may require dose adjustments or alternative treatments. Eliquis is metabolized by the liver and excreted by the kidneys, so proper function of these organs is essential for its safe use.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
The safety of Eliquis during pregnancy and breastfeeding has not been well-established. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should discuss the potential risks and benefits with their healthcare provider before starting Eliquis.
Surgical and Dental Procedures
Patients scheduled for surgery or dental procedures should inform their healthcare providers about their use of Eliquis. The medication may need to be temporarily discontinued to reduce the risk of bleeding during and after the procedure.
Conclusion
Eliquis is a powerful and effective anticoagulant that offers significant benefits for patients at risk of blood clots. Its advantages over traditional anticoagulants include a lower risk of major bleeding, predictable dosing, and no need for routine monitoring. However, it is essential for patients and healthcare providers to be aware of potential side effects and drug interactions to ensure its safe and effective use.